Inside this Article
Research Context and Its ImportanceDemographics, Workforce Growth, and Economic Integration of Automation and AIThe Development of Automation, Robotics, and AICountry-Specific Approaches to Automation and Workforce TransformationPros and Cons of Automation and AI in Workforce DynamicsPolicy Initiatives and Responsible Tech AdoptionMethodologyDiscussion

Countries worldwide face shifting workforce demographics driven by aging populations, declining birth rates, and technological advancements. But as new technologies are developed, nations and industries need to adopt policies that integrate artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and automation into the workforce effectively, while mitigating some of their more damaging impacts.
At Website Planet, we analyzed global workforce trends and their role in driving the adoption of automation and AI, aiming to inform our readers on how these shifts are shaping the future of work.
This article explores how a number of countries are leveraging automation, AI, and robotics in response to their unique social and economic challenges. In addition to examining national policies, it also assesses the benefits and challenges of integrating these technologies into the workforce.
Research Context and Its Importance
Countries worldwide are witnessing diverse demographic challenges, particularly the rise of aging workforces and a widening skill gap driven by rapid technological advancement.
This article examines data such as historical development of automation, robotics, and AI, workforce distributions, AI-focused national policies, and country-specific industry reliance on these technologies. By examining these elements, the article aims to highlight the benefits and limitations of the technologies, as well as their broader social and economic impacts.
Demographics, Workforce Growth, and Economic Integration of Automation and AI
Significant shifts in the global workforce, along with varied demographic pressures — for example, aging populations, changing youth demographics, and the need to boost efficiency and economic growth — are driving the global push toward integrating automation, robotics, and AI into the workforce.
In this section, we explore data on key demographic trends, including workforce growth by age group and GDP, to understand how these patterns influence an individual nation’s approach to adopting automation, robotics, and AI across economic sectors.
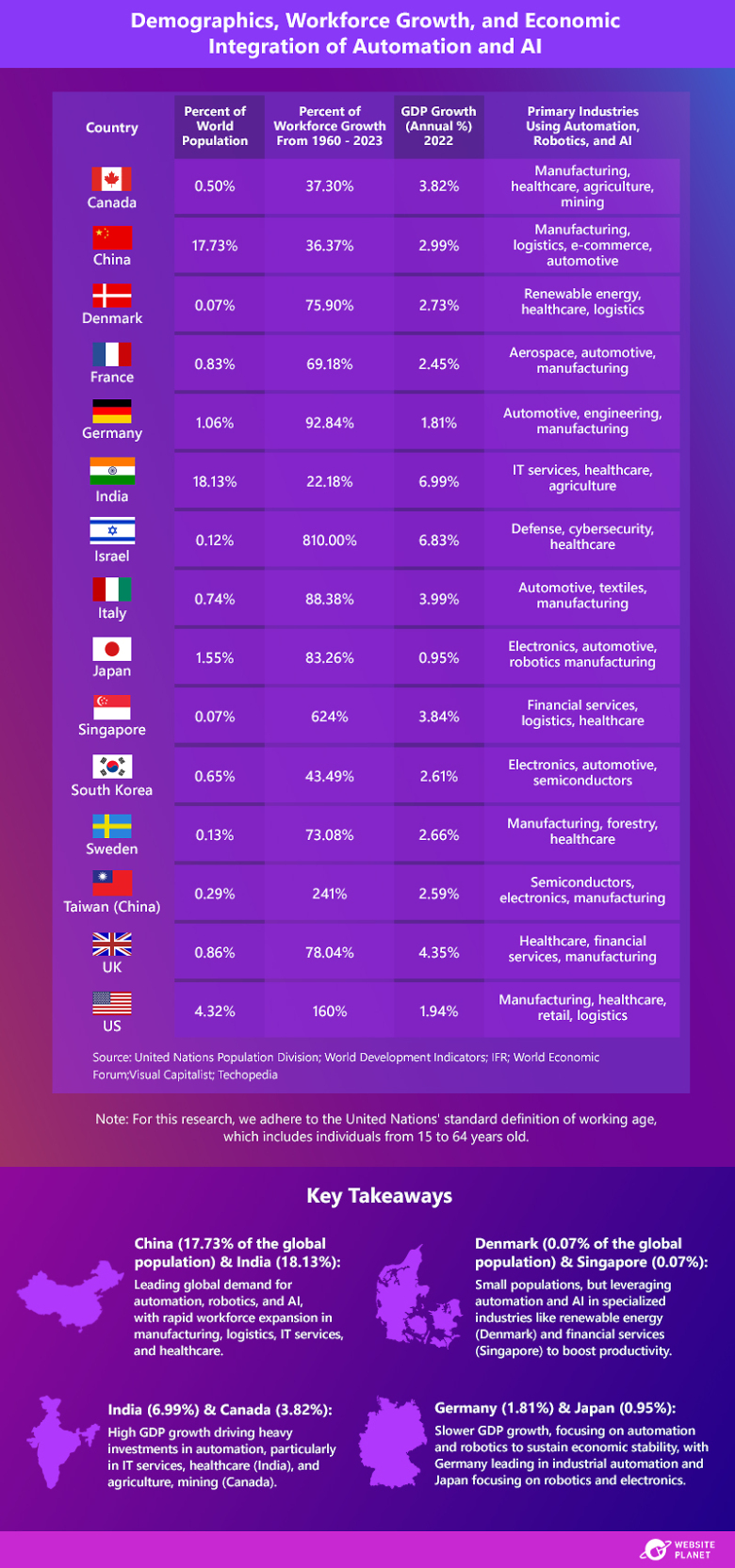 The graphic above highlights how countries, irrespective of their population size or economic growth rate, are increasingly turning to automation, robotics, and AI to boost productivity, address the rapidly changing labor demographics, and maintain their growth in global markets.
The graphic above highlights how countries, irrespective of their population size or economic growth rate, are increasingly turning to automation, robotics, and AI to boost productivity, address the rapidly changing labor demographics, and maintain their growth in global markets.
The Development of Automation, Robotics, and AI
Since the inception of AI in 1956, the world has witnessed a rapid acceleration in the field and in its adoption across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
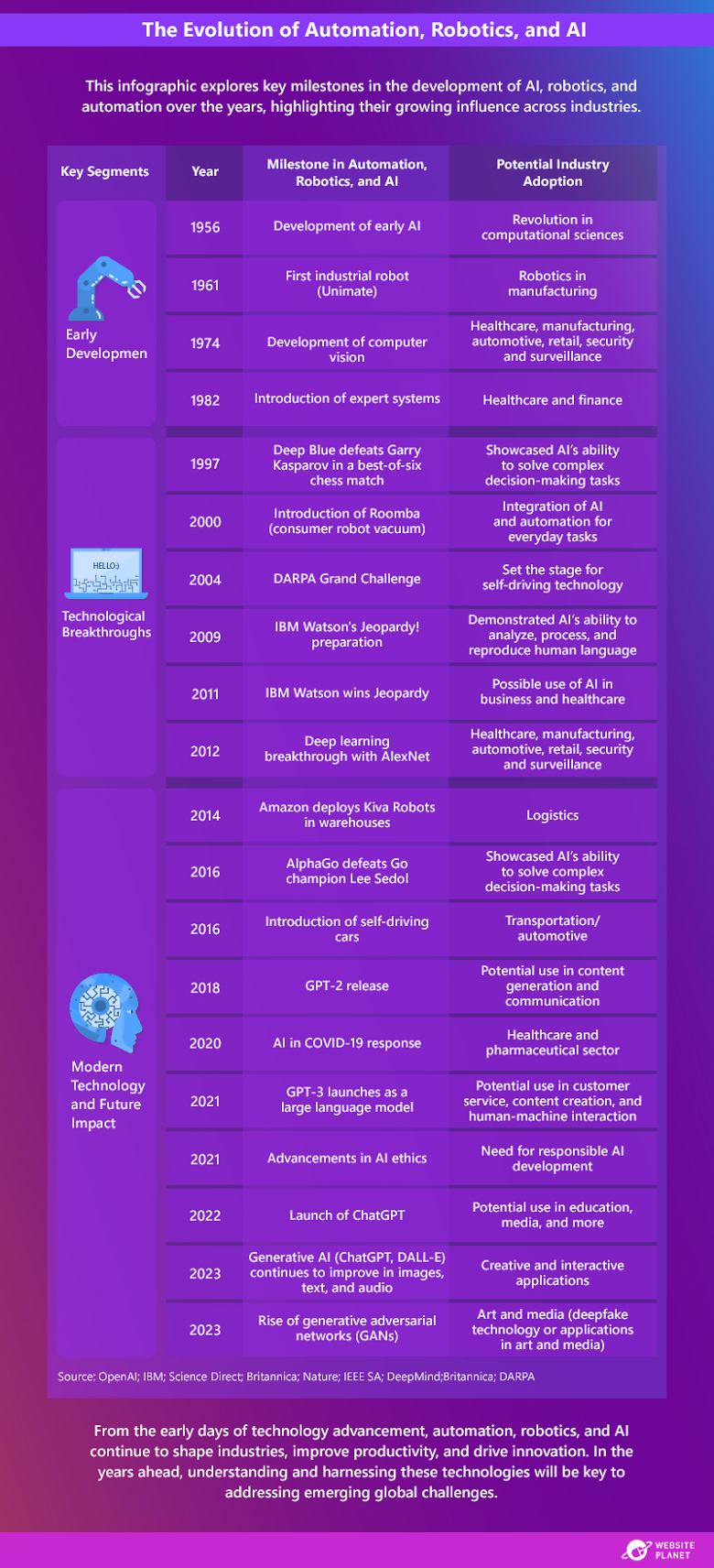 The graphic above illustrates the rapid and transformative shift in technology that has occurred across industries and everyday lives over the past several decades.
As automation and AI continue to be developed, new opportunities for industry adoption will continue to emerge, especially to improve efficiencies, address skill gaps, and streamline operations. While these technological advancements promise to transform industries and redefine the future of work, integrating them responsibly into the workforce is essential to maximize benefits and minimize potential drawbacks.
The graphic above illustrates the rapid and transformative shift in technology that has occurred across industries and everyday lives over the past several decades.
As automation and AI continue to be developed, new opportunities for industry adoption will continue to emerge, especially to improve efficiencies, address skill gaps, and streamline operations. While these technological advancements promise to transform industries and redefine the future of work, integrating them responsibly into the workforce is essential to maximize benefits and minimize potential drawbacks.
Country-Specific Approaches to Automation and Workforce Transformation
As global population trends diverge, with some countries experiencing rapid growth and others facing population decline, nations are increasingly turning to automation, AI, and robotics to address their unique workforce challenges.
Countries with relatively low birth rates and aging demographics, such as Italy, Japan, and Germany, are adopting technology to address labor shortages. In contrast, countries with high population growth, like India, Nigeria, and Indonesia, have younger populations and expanding industries that are driving demand for productivity-enhancing technologies.
Automation and Workforce Innovation in Countries With Aging Populations
In countries with aging populations, governments and industries are turning to automation, AI, and robotics to address workforce gaps and maintain productivity levels.
This section evaluates how these countries are strategically adopting these technologies to transform their workforce, including deploying tailored, industry-specific initiatives.
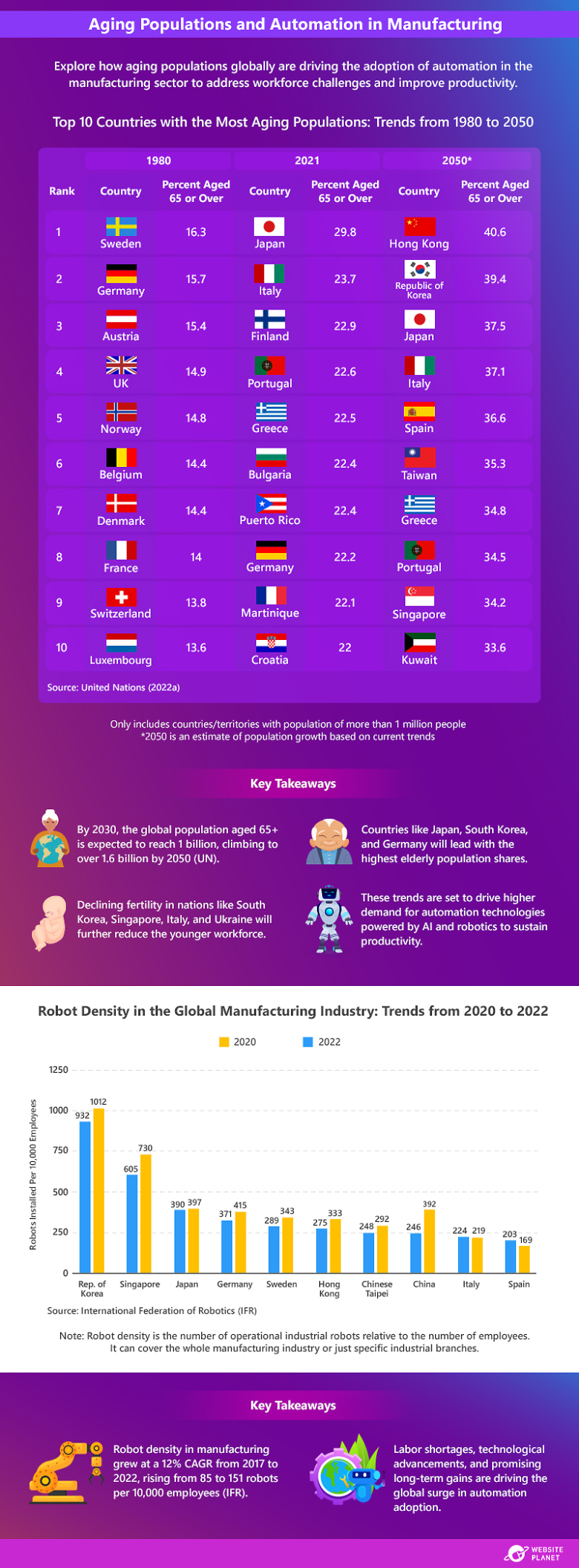 According to the UN, workforce challenges due to an aging population will not be limited to developed countries; many developing economies are projected to experience similar struggles in the coming decades. The 2023 International Federation of Robotics (IFR) report highlights that nations such as India (8,510 units), Mexico (5,832 units), and Turkey (4,400 units) are already emerging as key markets for industrial robot installations, ranking among the top 15 markets worldwide.
Simultaneously, the growing advancement in and adoption of AI and machine learning is already reshaping enterprises worldwide. According to Grand View Research, the global AI market is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.6% from 2024 to 2030.
These developing technologies, in combination with the aging populations and shrinking workforces, are driving investment in automation to address labor shortages, improve efficiencies, and sustain economic productivity.
According to the UN, workforce challenges due to an aging population will not be limited to developed countries; many developing economies are projected to experience similar struggles in the coming decades. The 2023 International Federation of Robotics (IFR) report highlights that nations such as India (8,510 units), Mexico (5,832 units), and Turkey (4,400 units) are already emerging as key markets for industrial robot installations, ranking among the top 15 markets worldwide.
Simultaneously, the growing advancement in and adoption of AI and machine learning is already reshaping enterprises worldwide. According to Grand View Research, the global AI market is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36.6% from 2024 to 2030.
These developing technologies, in combination with the aging populations and shrinking workforces, are driving investment in automation to address labor shortages, improve efficiencies, and sustain economic productivity.
Expanding Automation Opportunities in High-Growth Markets
Countries with high-growth demographics like India, China, Brazil, and Mexico are well positioned to leverage automation, AI, and robotics due to their youthful populations, rapid urbanization, and expanding industries.
This section examines how these technologies are gaining momentum across key sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and manufacturing to address workforce shortages, enhance productivity, and sustain economic development.
 As seen in the graphic above, China leads in industrial automation and AI adoption among the selected high-growth markets, while countries like India and Brazil are gradually automating sectors like agriculture and manufacturing.
Despite challenges such as infrastructure gaps, these regions show strong potential for technological advancement and economic growth.
As seen in the graphic above, China leads in industrial automation and AI adoption among the selected high-growth markets, while countries like India and Brazil are gradually automating sectors like agriculture and manufacturing.
Despite challenges such as infrastructure gaps, these regions show strong potential for technological advancement and economic growth.
Diverse Global Approaches to Automation and AI Integration
This section explores how automation, robotics, and AI are adapted across various economies, each with unique economic landscapes and workforce challenges. From highly industrialized nations like the US, Germany, and Japan to fast-growing markets such as India and Israel, the analysis shows how these technologies address demographic shifts, enhance productivity, and drive key industries like automotive, semiconductors, and financial services.
By examining these varied approaches, we gain insights into how technologies foster global economic resilience and workforce transformation.
 The analysis highlights the diverse use of these technologies across different economies. Developed countries like the US, Germany, and Japan focus on robotics and AI to increase productivity in industries such as automotive, healthcare, and electronics. In contrast, emerging markets like India and Israel concentrate on AI-driven innovations in IT, finance, and defense.
The analysis highlights the diverse use of these technologies across different economies. Developed countries like the US, Germany, and Japan focus on robotics and AI to increase productivity in industries such as automotive, healthcare, and electronics. In contrast, emerging markets like India and Israel concentrate on AI-driven innovations in IT, finance, and defense.
Pros and Cons of Automation and AI in Workforce Dynamics
The integration of automation, robotics, and AI into the workforce across industries is expected to enhance productivity, improve safety standards, and drive economic growth. A March 2023 report by Goldman Sachs projects that broad AI adoption could raise global GDP by up to 7% annually over a 10-year period, due to productivity gains.
However, while these technologies provide notable benefits in innovation and efficiency, they also present challenges, such as job displacement, skill gaps, high implementation costs, and environmental concerns due to high energy demands of AI training and use.
A January 2024 IMF study found that AI could impact up to 60% of jobs in developed countries, with around 30% of these leading to adverse effects on the workforce. In contrast, emerging markets and lower-income countries may see AI impacting about 40% and 26% of jobs, respectively.
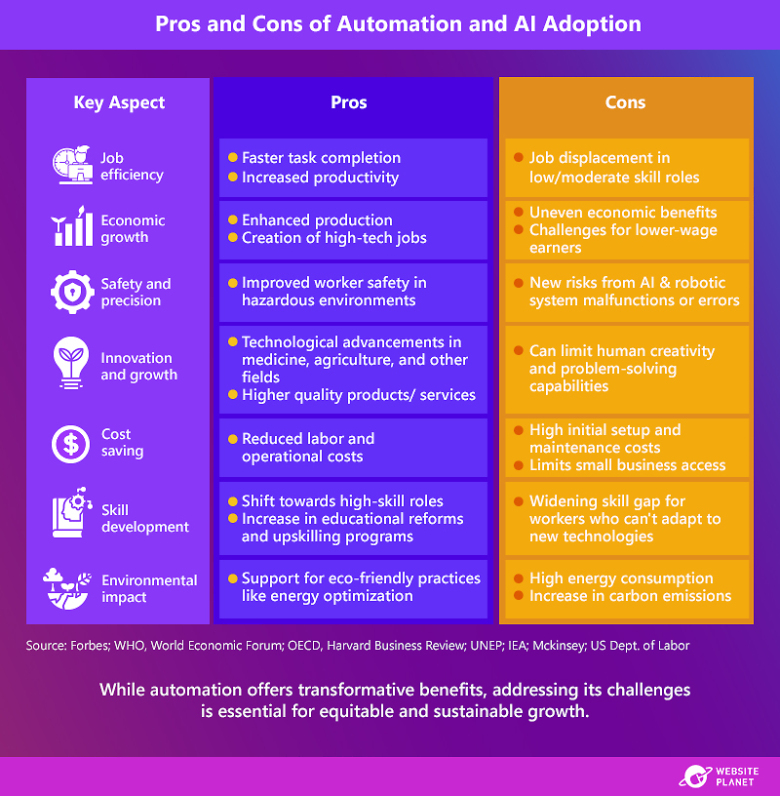 This graphic highlights advantages and drawbacks of AI, robotics, and automation across key aspects like efficiency, economic growth, and more. To fully harness the benefits of these technologies, technological advancements need to be balanced with national and industrial policies that support reskilling, equitable economic distribution, and responsible environmental practices.
This graphic highlights advantages and drawbacks of AI, robotics, and automation across key aspects like efficiency, economic growth, and more. To fully harness the benefits of these technologies, technological advancements need to be balanced with national and industrial policies that support reskilling, equitable economic distribution, and responsible environmental practices.
Policy Initiatives and Responsible Tech Adoption
As automation, AI, and robotics continue to reshape global labor markets, governments worldwide are developing and implementing policies and initiatives to ensure responsible adoption of these technologies.
From funding research programs to designing regulatory frameworks, governments are focused on maximizing the benefits of these innovations to support the development of the workforce and society as a whole.
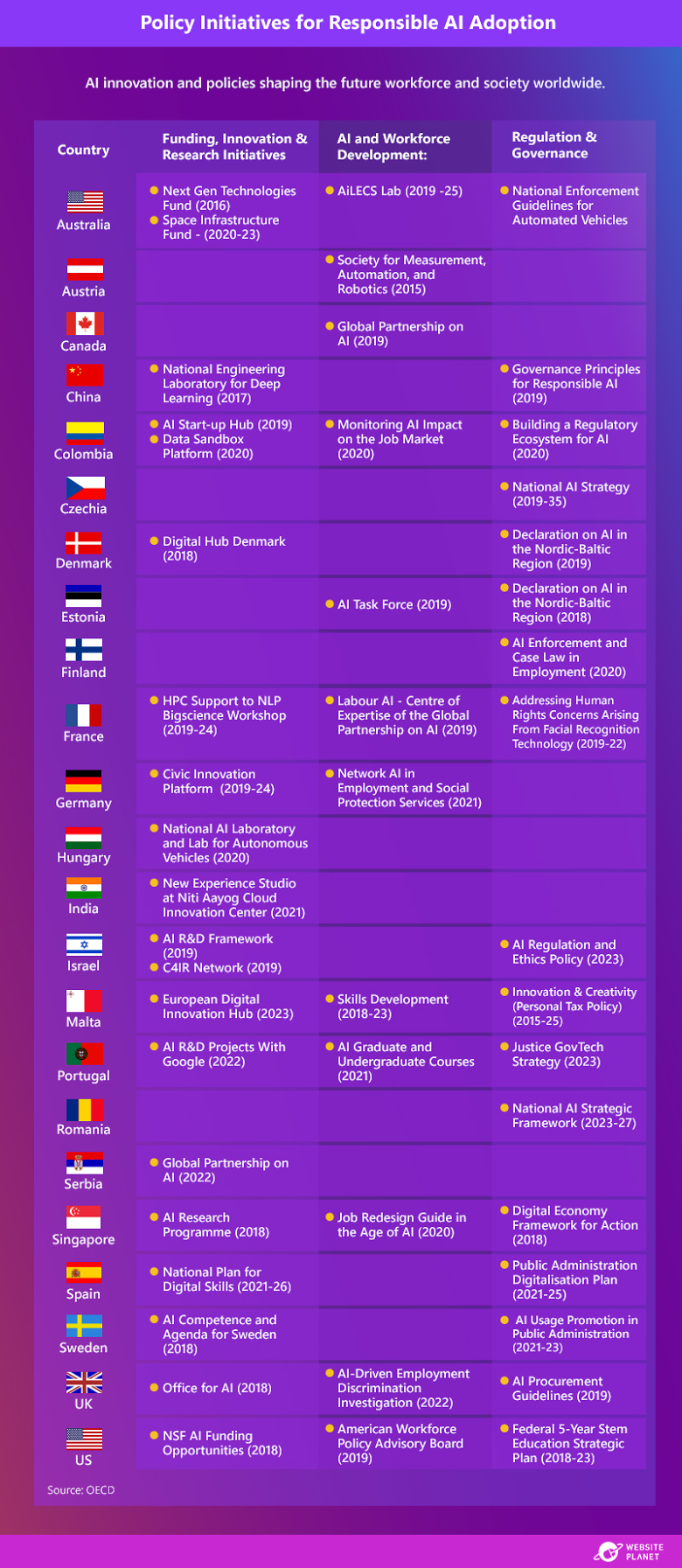 Globally, countries are responding to rapid technological advancements with tailored strategies that aim to promote ethical innovation and reduce job displacement risks through investment in reskilling programs. For example, countries like the US, Australia, and China have prioritized funding for AI R&D and regulatory frameworks, while others like Colombia and Portugal focus on regional AI ecosystems and educational programs.
These initiatives reflect a global commitment by countries to balance technological advancements with workforce development.
Globally, countries are responding to rapid technological advancements with tailored strategies that aim to promote ethical innovation and reduce job displacement risks through investment in reskilling programs. For example, countries like the US, Australia, and China have prioritized funding for AI R&D and regulatory frameworks, while others like Colombia and Portugal focus on regional AI ecosystems and educational programs.
These initiatives reflect a global commitment by countries to balance technological advancements with workforce development.